AWS Databases
I'll be briefly covering databases which AWS provide as well as the key features that each service offer. I've also listed ports at the end to be familiar with.
Database Types
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
This service allows you to create a database in the cloud. You can choose from the following:This service is managed by AWS which means you won't be able to SSH into the instance but you do benefit from a list of services:
If you would like the option to have access to your RDS instance then there is 'RDS Custom' which allows you access to the underlying database and OS so you can configure and install patches yourself if that's a use case you require.
Auto Scaling Storage
This feature helps increase the storage on an RDS instance when it's running out of free space and it will do it automatically. You do have to set the 'Maximum Storage Threshold'. This feature can help with unpredictable workloads and supports all RDS database instances.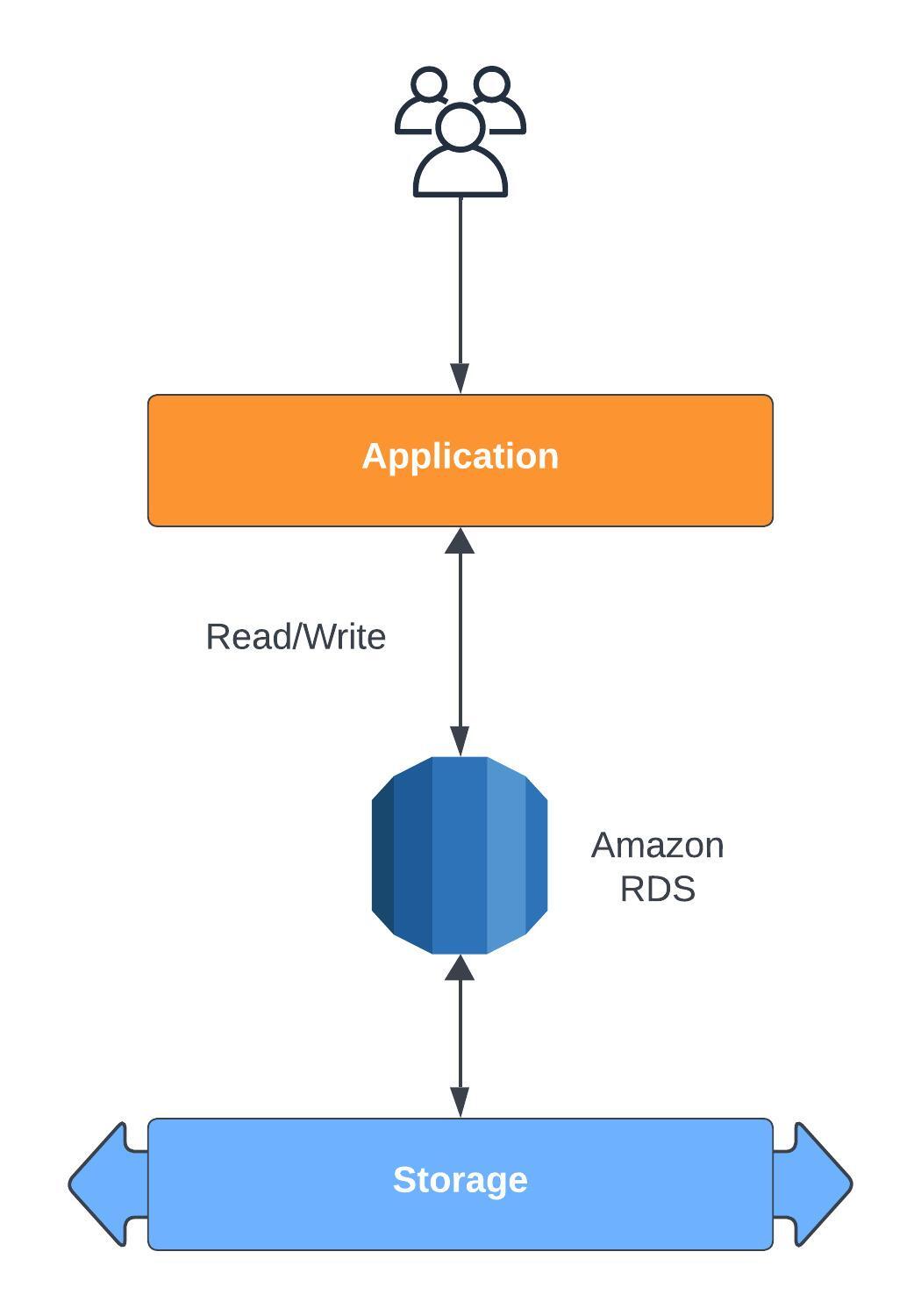
Read Replicas
RDS allows up to 15 read replicas within the same availability zone, across multiple availability zones or even cross region. It's also possible to take a replica read instance and make it the main RDS instance. The replication is ASYNC, meaning that the data will eventually be consistent. You can only query (SELECT) data from a read replica not do any manipulations such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE queries.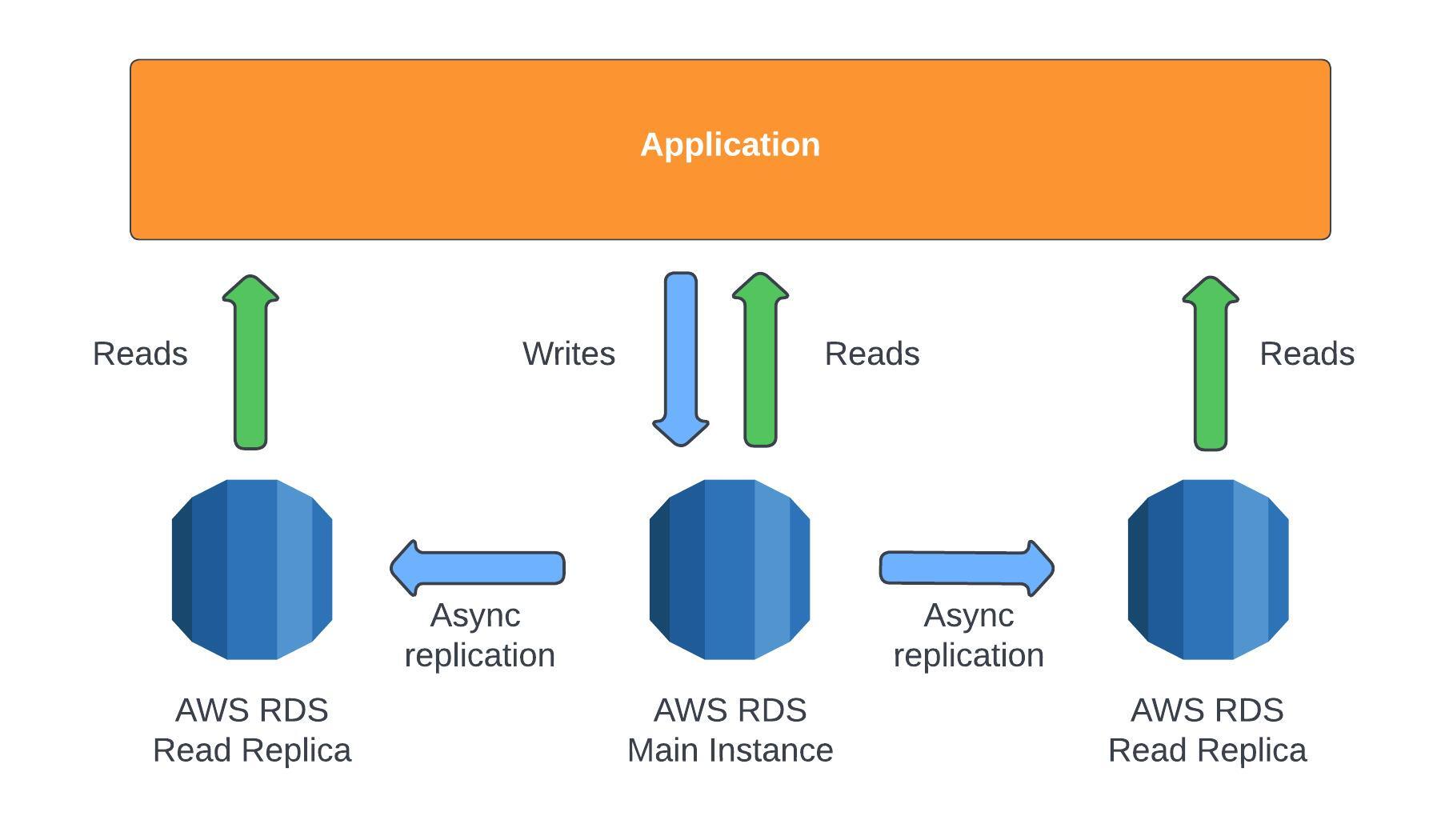 It's important to note that there is a network cost for transferring data into another availability zone; the only use-case where that doesn't apply is if it's within the same region and your transferring to a read replica instance.
It's important to note that there is a network cost for transferring data into another availability zone; the only use-case where that doesn't apply is if it's within the same region and your transferring to a read replica instance.RDS Multi AZ
Multi AZ is mainly used for disaster recovery. The application will read/write to the main RDS instance via one DNS name, and that instance will be making a SYNC replication, meaning a real time exchange of information to a standby instance in another availability zone. That means every change that the application is sending to the main instance, the main instance will have to update the standby instance. If there is a problem with the main instance then there will be an automatic failover to the standby instance. This failover could happen due to network issues or instance/storage failure, if any of these events occur the standby instance would be promoted to the main instance. It's possible to setup read replicas for Multi AZ.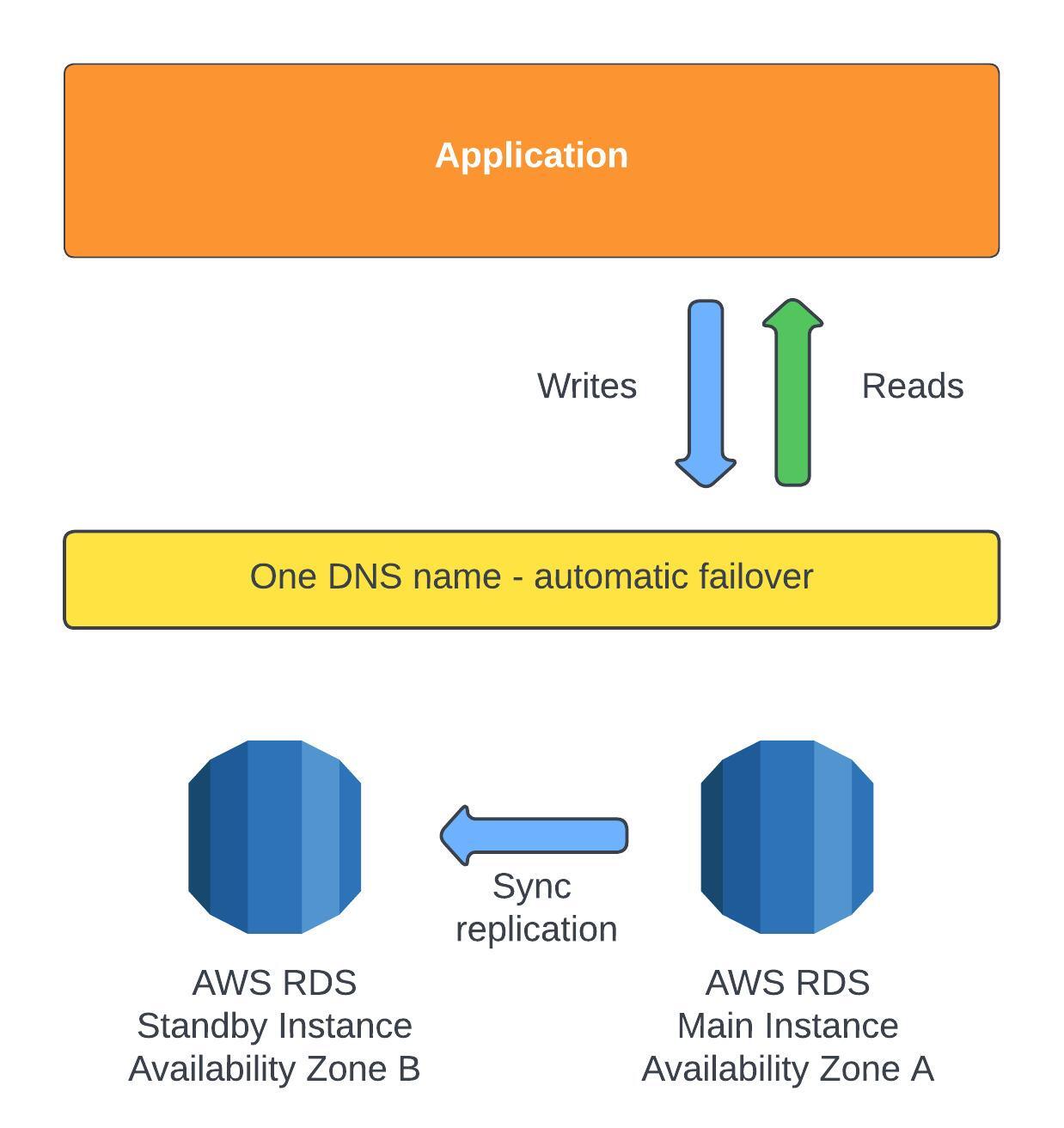 There isn't any downtime for this process to happen, nor you need to modify your application as RDS handles this process in the background when configured. Here is a brief explanation of what happens. MultiAZBackground
There isn't any downtime for this process to happen, nor you need to modify your application as RDS handles this process in the background when configured. Here is a brief explanation of what happens. MultiAZBackground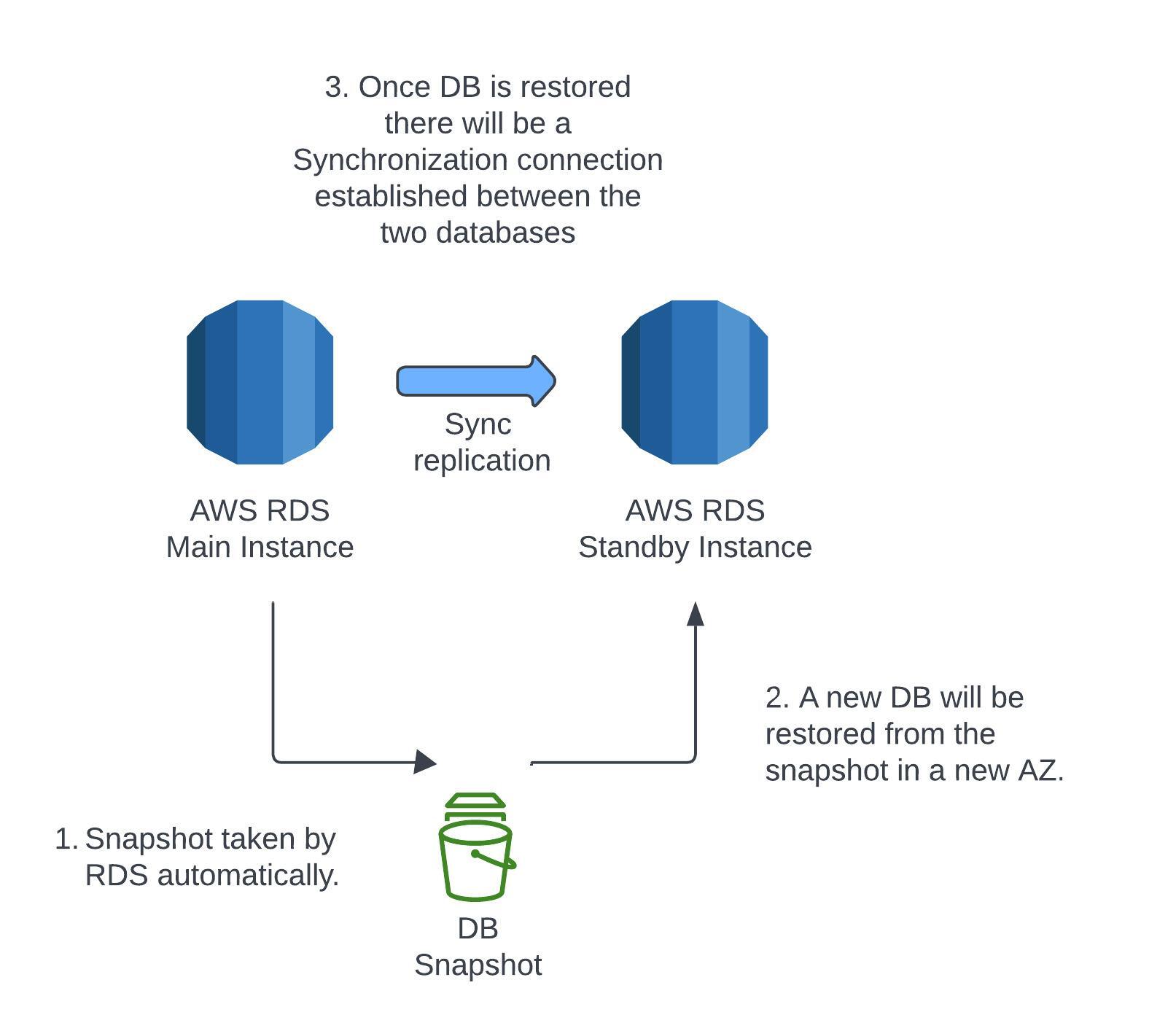
RDS Backups
RDS has the ability to backup instances either automatically or manually. You can do a full backup of the database daily with the ability to restore to any point in time from oldest to five minutes ago. Transaction logs are backed up by RDS every five minutes. There is a retention period up to 35 days for automatic backups but can last as long as you want if backed up manually. Automated backups can be disabled. Do note that a stopped RDS instance still costs money as you're still paying for the existing storage. If you plan on stopping it for a long period of time, you should snapshot and restore instead.RDS Restore
RDS has the ability to restore an instance by creating a backup of the existing database which is stored in S3, that is then used on a new RDS instance running MySQL.RDS Proxy
This allows apps to pool and share database connections already established. Instead of having individual applications connect to the RDS instance, they will instead connect to the proxy which will pool the connections together into less connections to the RDS instance. You would want to do this to improve the database efficiency by reducing the strain on the RDS resources such as CPU and RAM. This feature auto-scales and is multi-AZ so you won't need to manage capacity which in turn reduces the failover time by up to 66%. This feature enforces IAM authentication, so users can only connect to the RDS instance using the correct credentials, and it's never publicly available as it can only be accessed from a VPC. This supports RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MSSQL Server) and Aurora (MySQL and PostgreSQL).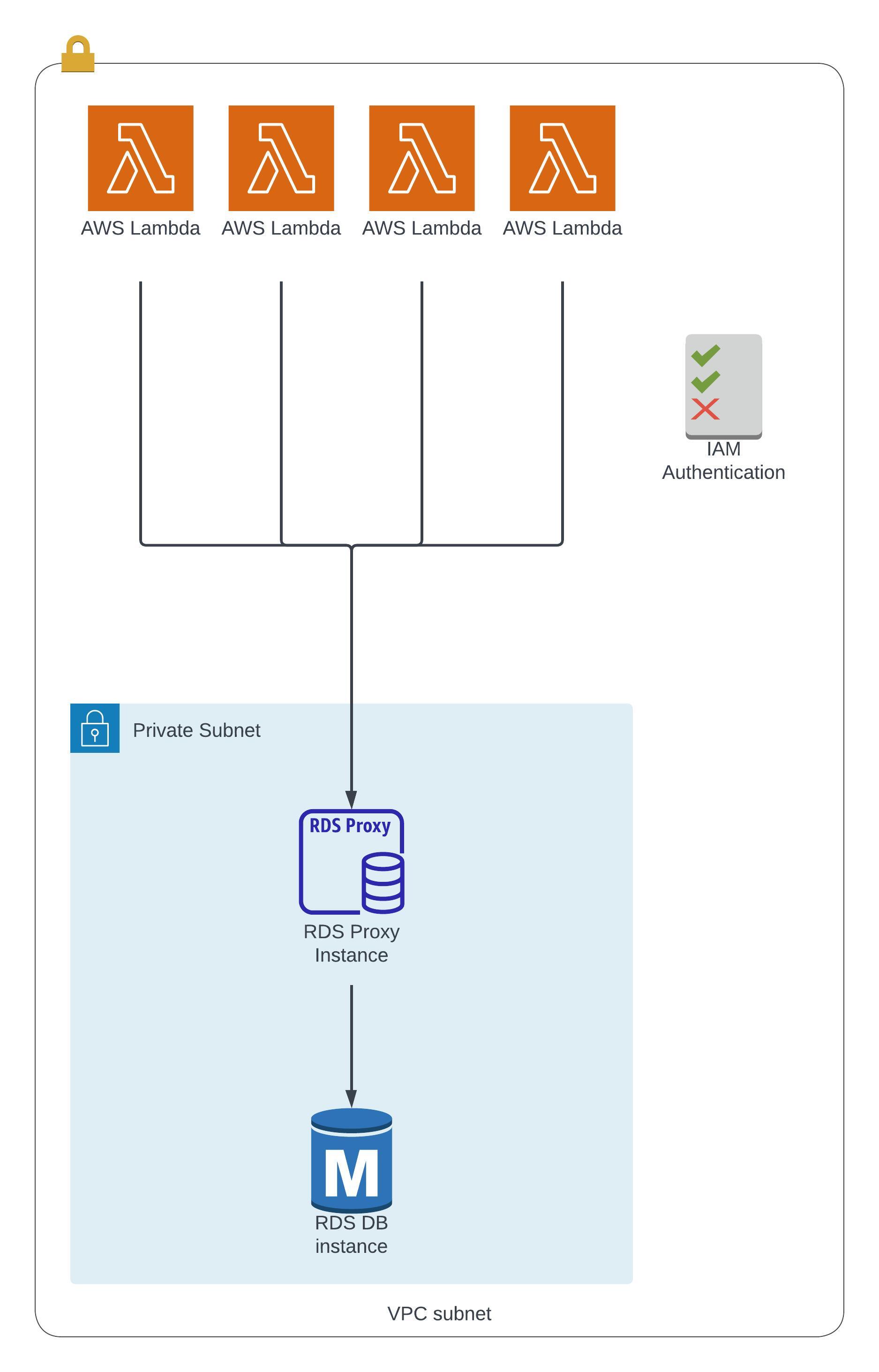
Invoking Lambda from RDS & Aurora
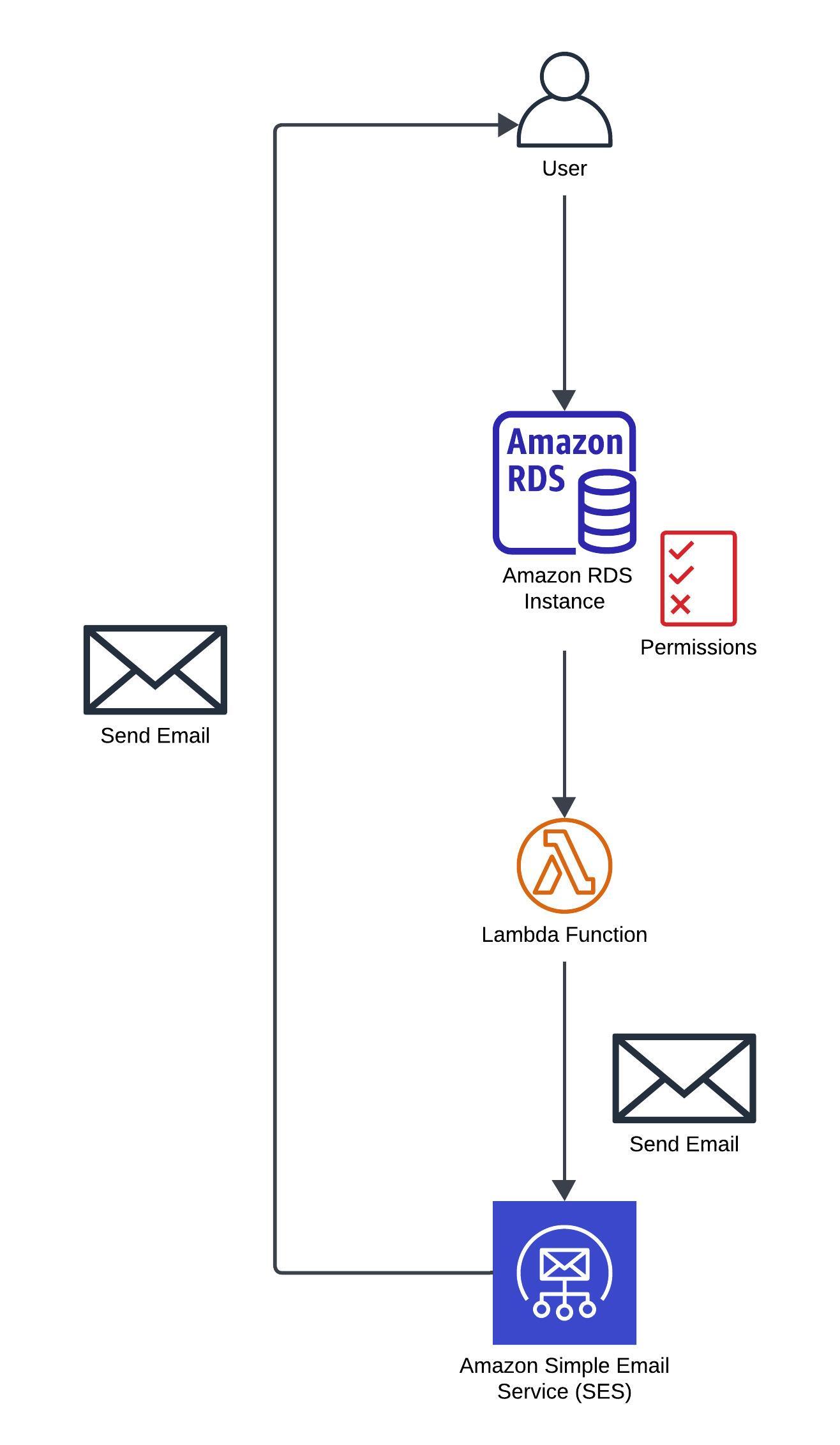
RDS Event Notifications
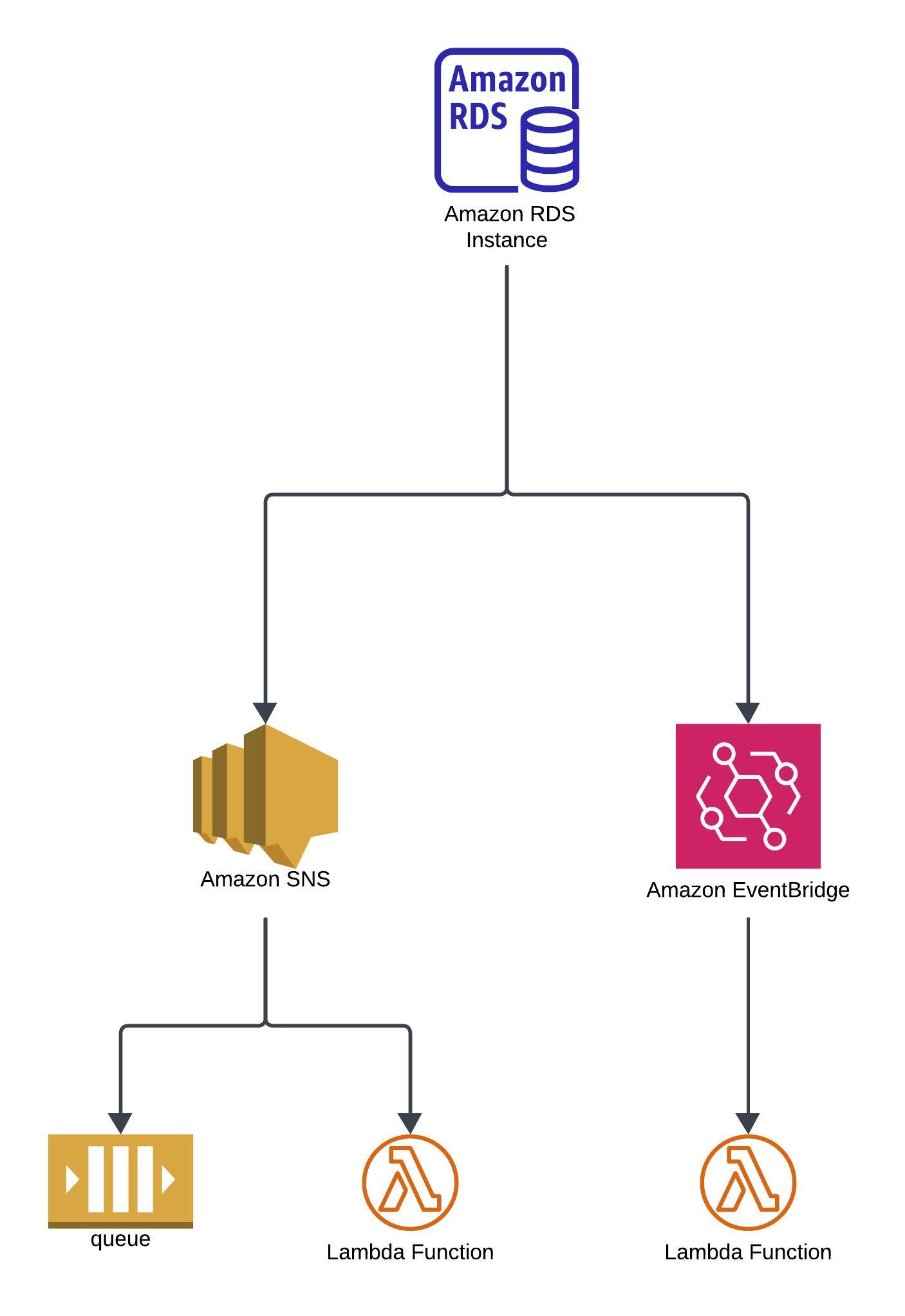
RDS Summary
Amazon Aurora
Aurora is a cloud optimized database which has significant performance improvements over RDS. It has a capacity of up to 128 TB (terabytes) and grows in increments of 10 GB (gigabytes). Aurora can have up to 15 replicas and it's failover is instantaneous (30 seconds) but it all comes at a cost as it's roughly 20% more than an RDS instance.Features of Aurora
Aurora has high availability and reading scaling as it copies the data across three availability zones with six copies and the storage is striped across 100's of volumes every time you write to the database.
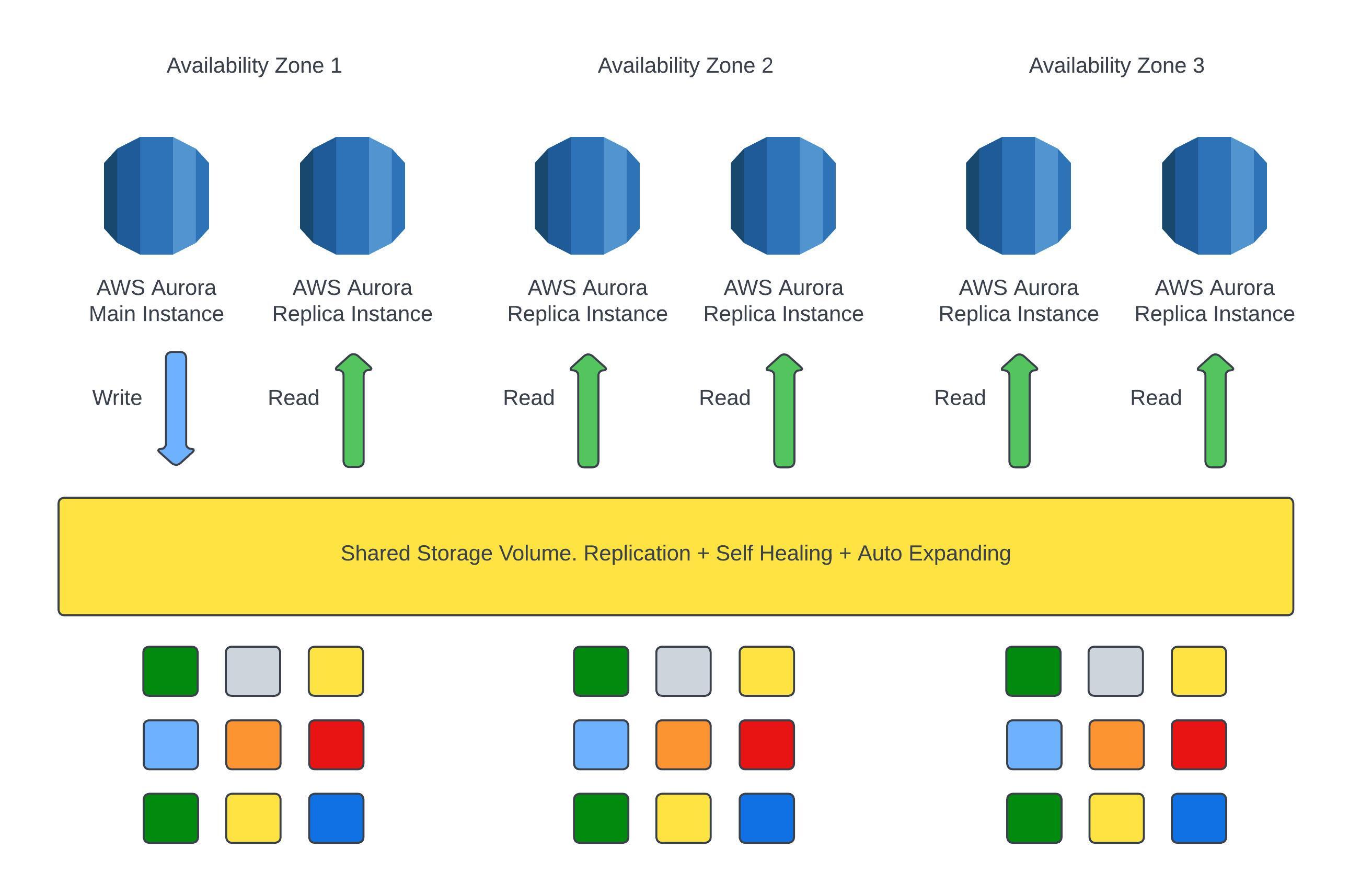
Aurora DB Cluster
Below shows how you would interact with an Aurora instance and how the clusters work. You will be given two endpoints, read and write, the write endpoint will always connect to the main instance which is the only instance to write to the storage, whereas the read endpoint connects to the read replicas.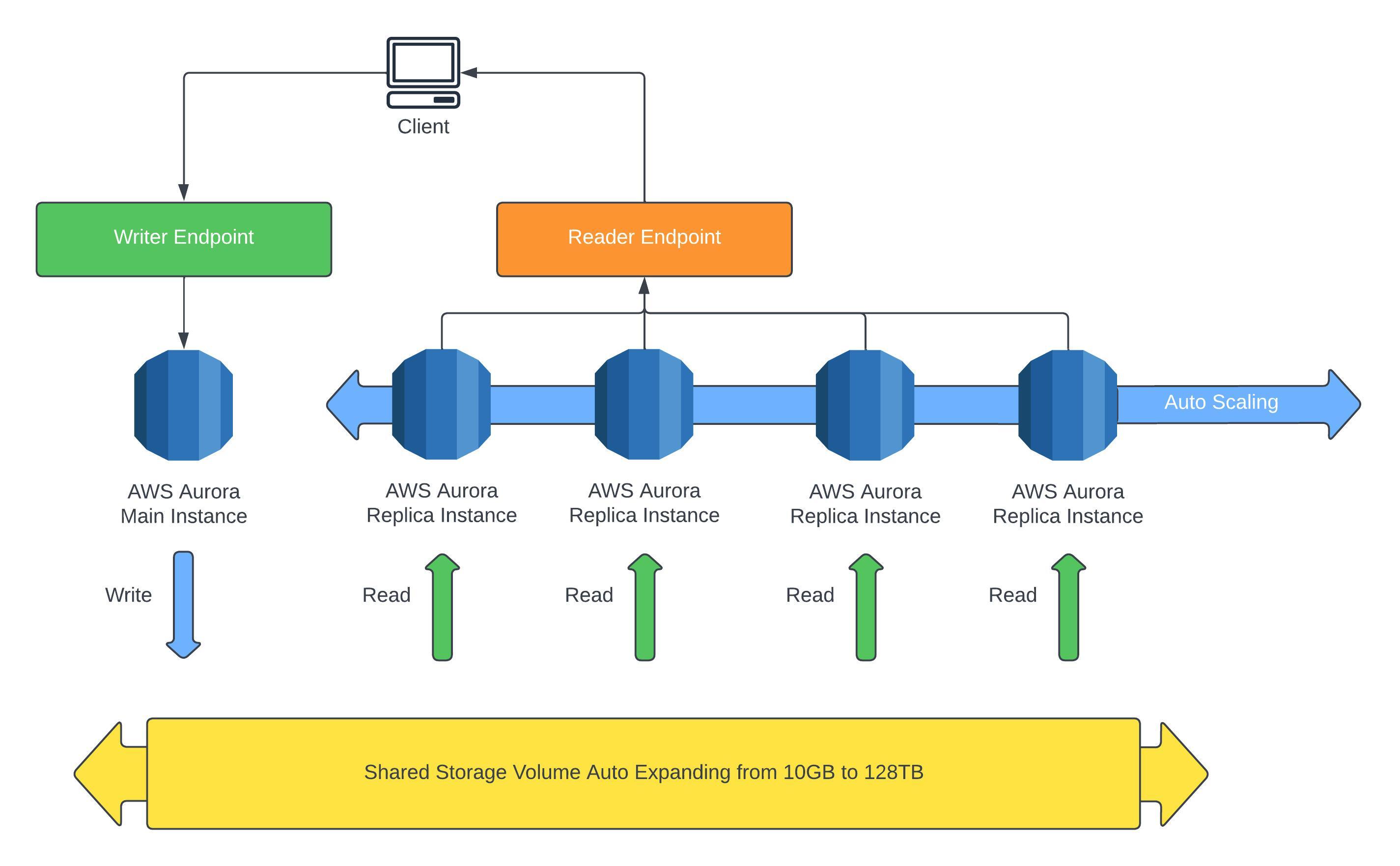
Aurora Custom Endpoints
If you wish to run analytics on the database without effecting performance you can define a subset of Aurora instances to point towards a custom endpoint.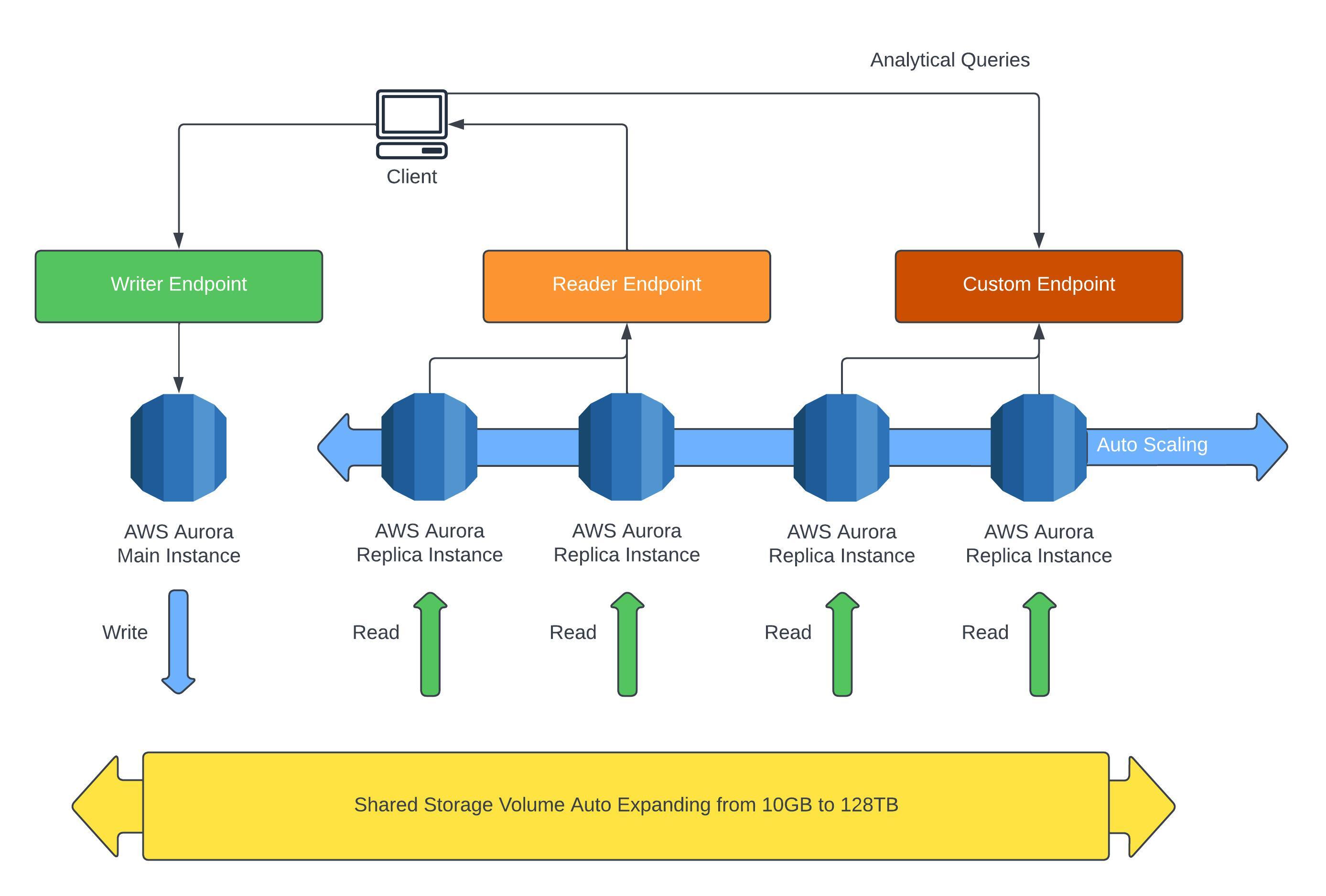
Aurora Serverless
Aurora Serverless is an automated database which auto scales based on usage. This could be good for infrequent, intermittent or unpredictable workloads.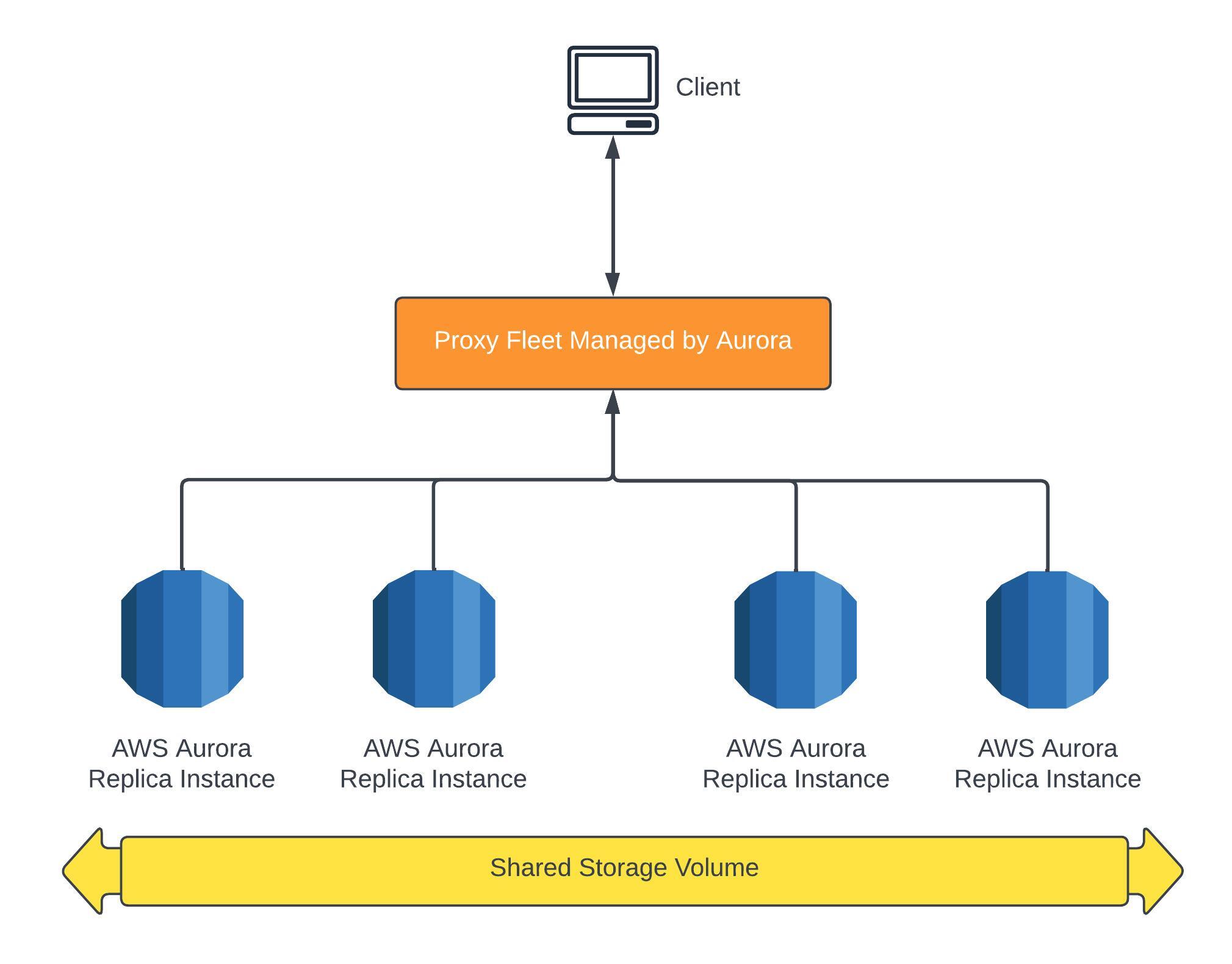
Aurora Global
Global Aurora has cross region read replicas which is good for disaster recovery. It takes less than a second to replicate data into another region.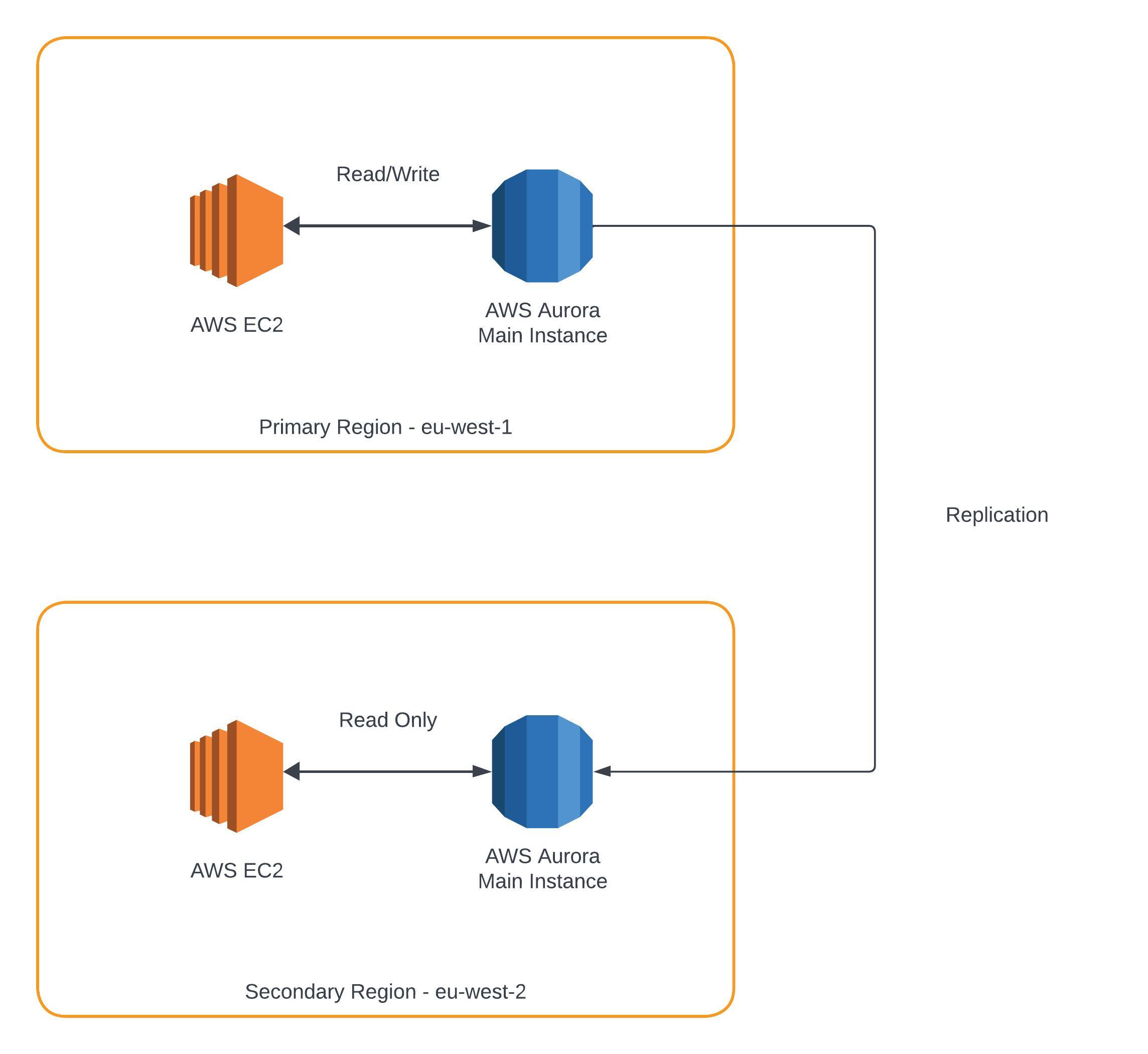
Aurora Machine Learning
You can integrate Aurora with machine learning services (AWS Sagemaker and AWS Comprehend) to make predictions with your applications via SQL. Good use cases for this would be to check for fraud detection and product recommendations.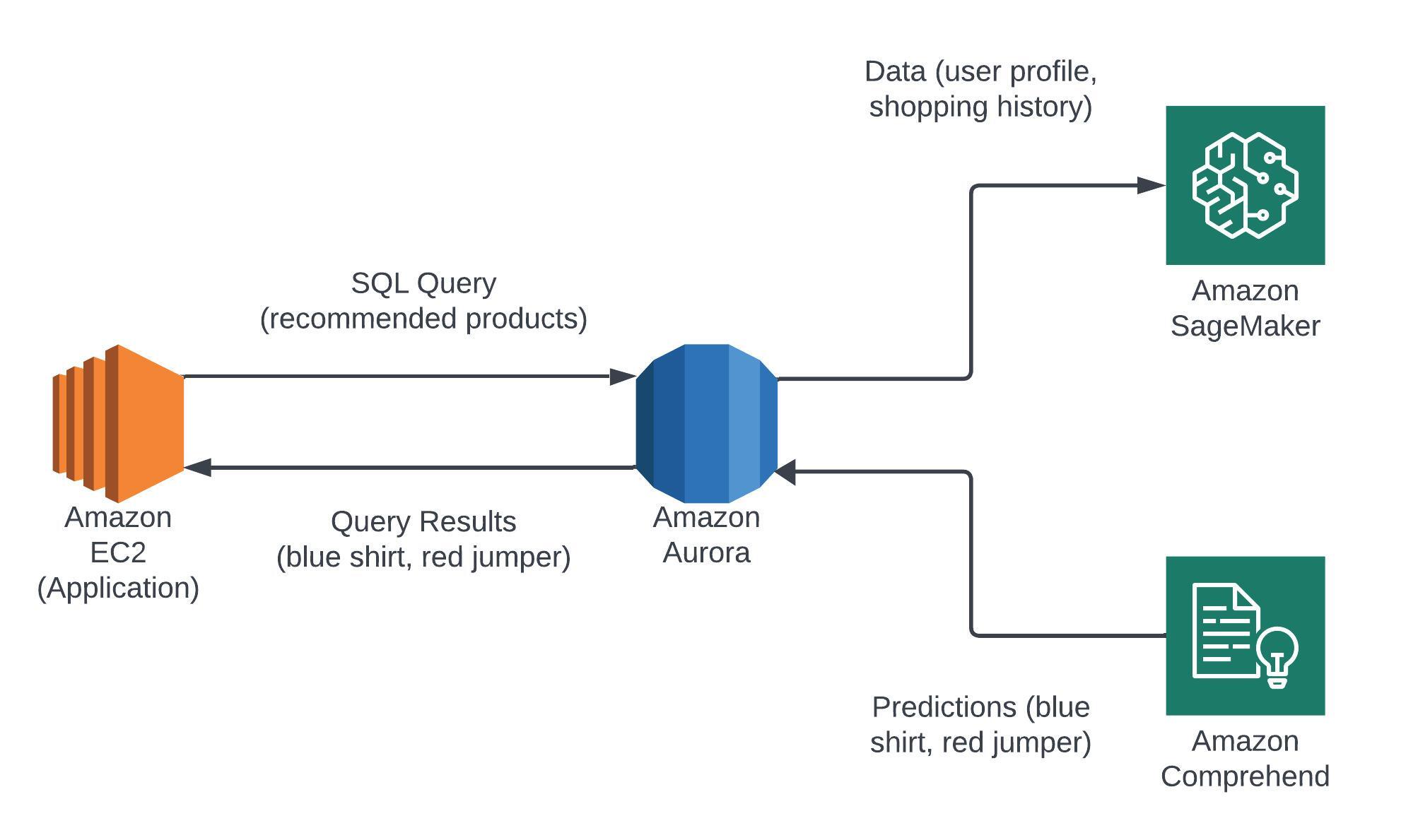
Aurora Backups
Aurora has the ability to backup instances either automatically or manually. You can do a full backup of the database daily with the ability to restore to any point in time. There is a retention period up to 35 days for automatic backups but can last as long as you want if backed up manually. Automated backups can't be disabled.Aurora Restore
Aurora has the ability to restore an instance by creating a backup of the existing database using Percona XtraBackup which is stored in S3, that is then used on a new Aurora cluster running MySQL.Aurora Cloning
Another feature of Aurora is that you can clone an existing database cluster from an existing one. This is faster than snapshot & restore and uses copy-on-write protocol. This feature is useful for creating a staging environment from a production database without impacting the live service.RDS & Aurora Security
Both RDS and Aurora have:Aurora Summary
Elasticache
ElastiCache is an in memory database which helps high performance and low latency (Redis or Memcached). This also helps makes applications stateless and reduces the load off of database for read intensive workloads. Like RDS and Aurora, AWS takes care of the OS maintenance/patching, optimisations, setup, configuration, monitoring, failure recovery and backups. Using ElastiCache does involve a lot of application code changes.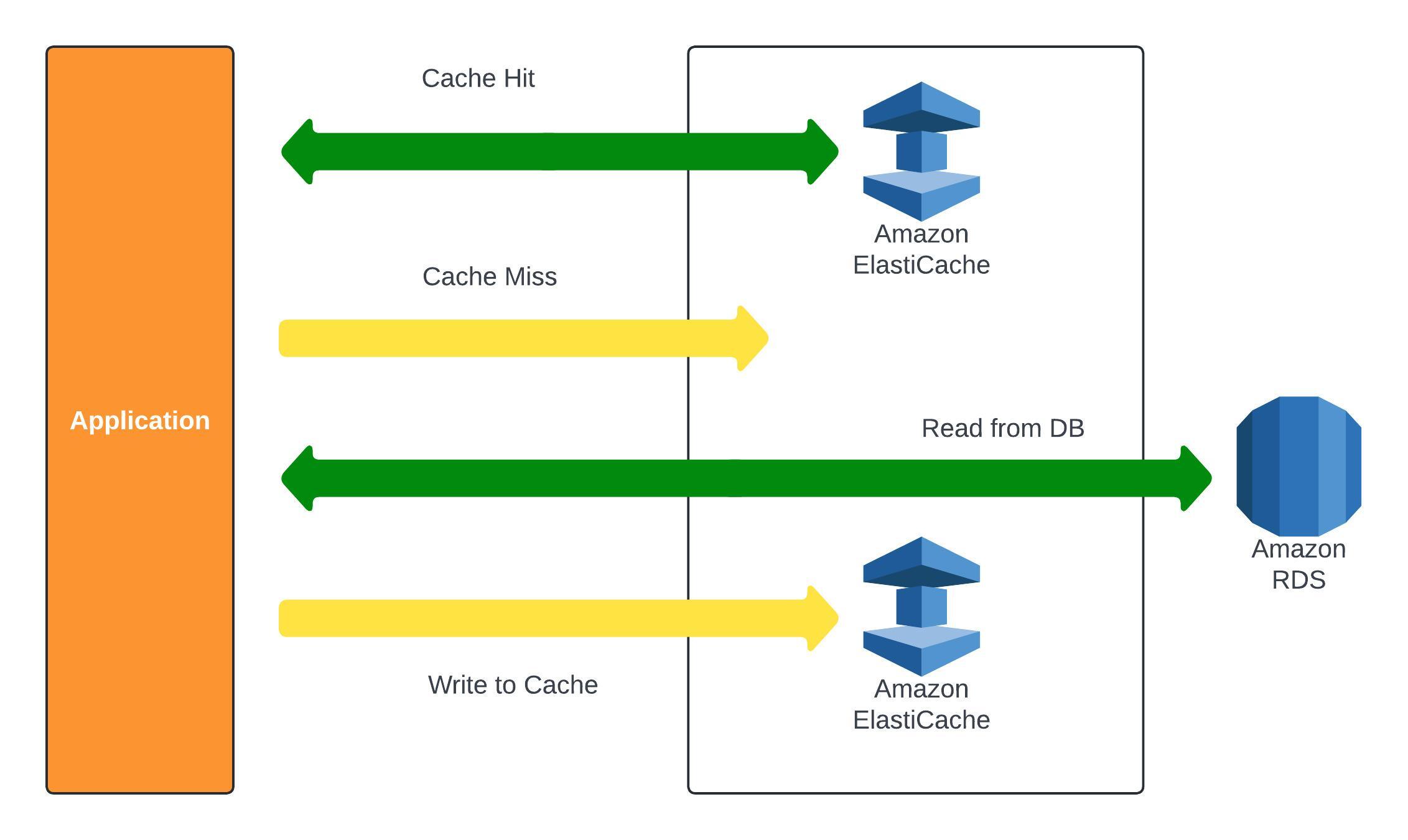
Redis vs Memcached
| Redis | Memcached |
|---|---|
| Multi AZ with Auto-Failover | Multi-node for partitioning of data (sharding) |
| Read Replicas to scale reads and have high availability | No high availability (replication) |
| Data durability using AOF persistence | Non persistent |
| Backup and restore features | No backups or restore |
| Supports Sets and Sorted sets | Multi-threaded architecture |
Cache Security
Elasticache supports IAM Authentication for Redis - the IAM policies are only used for AWS API-level security.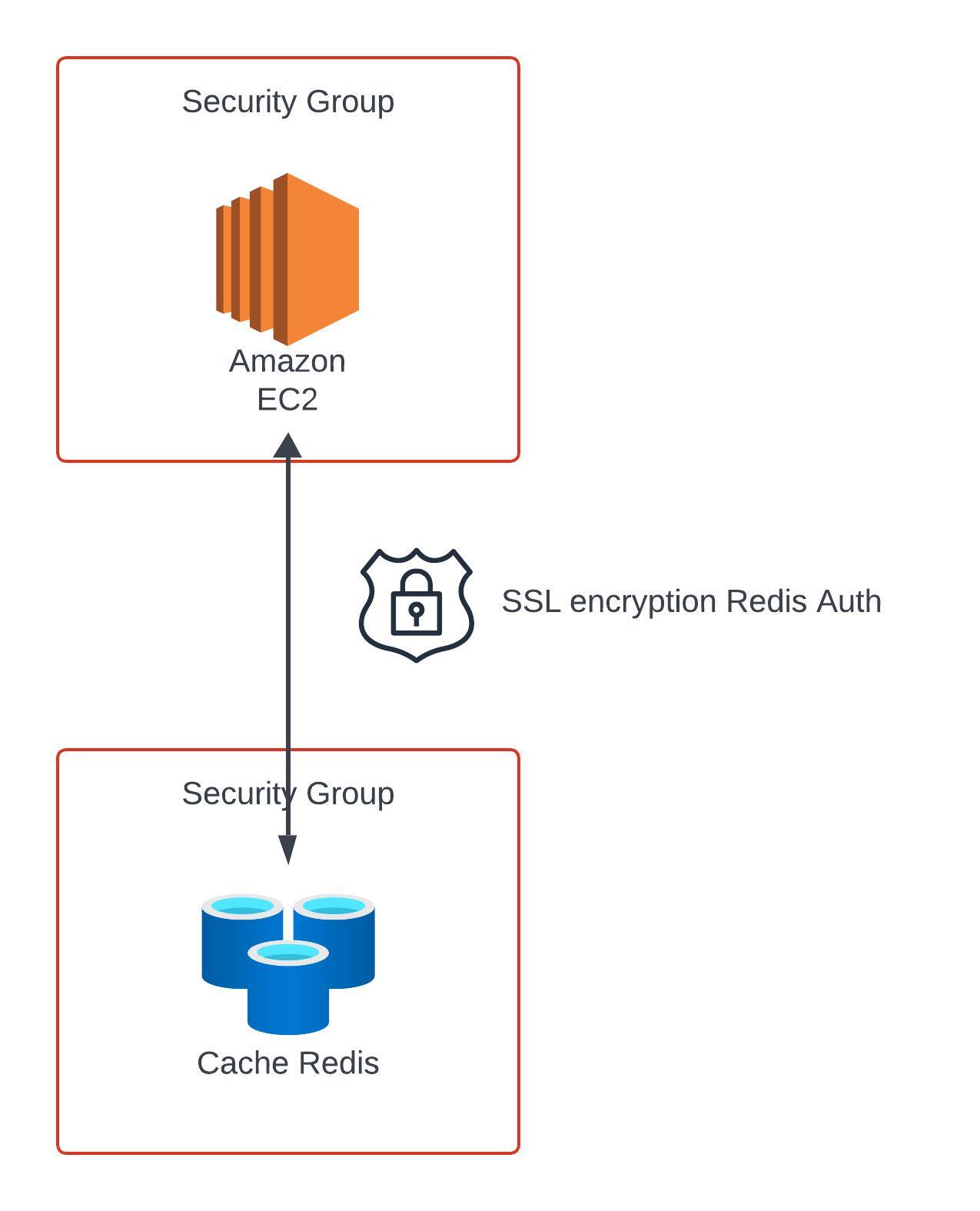
ElastiCache Summary
Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service. It is designed to offer fast, consistent, and scalable performance for applications that require low-latency data access, even as they scale to handle millions of requests per second.Read/Write Capacity Modes
DynamoDB Advanced Features
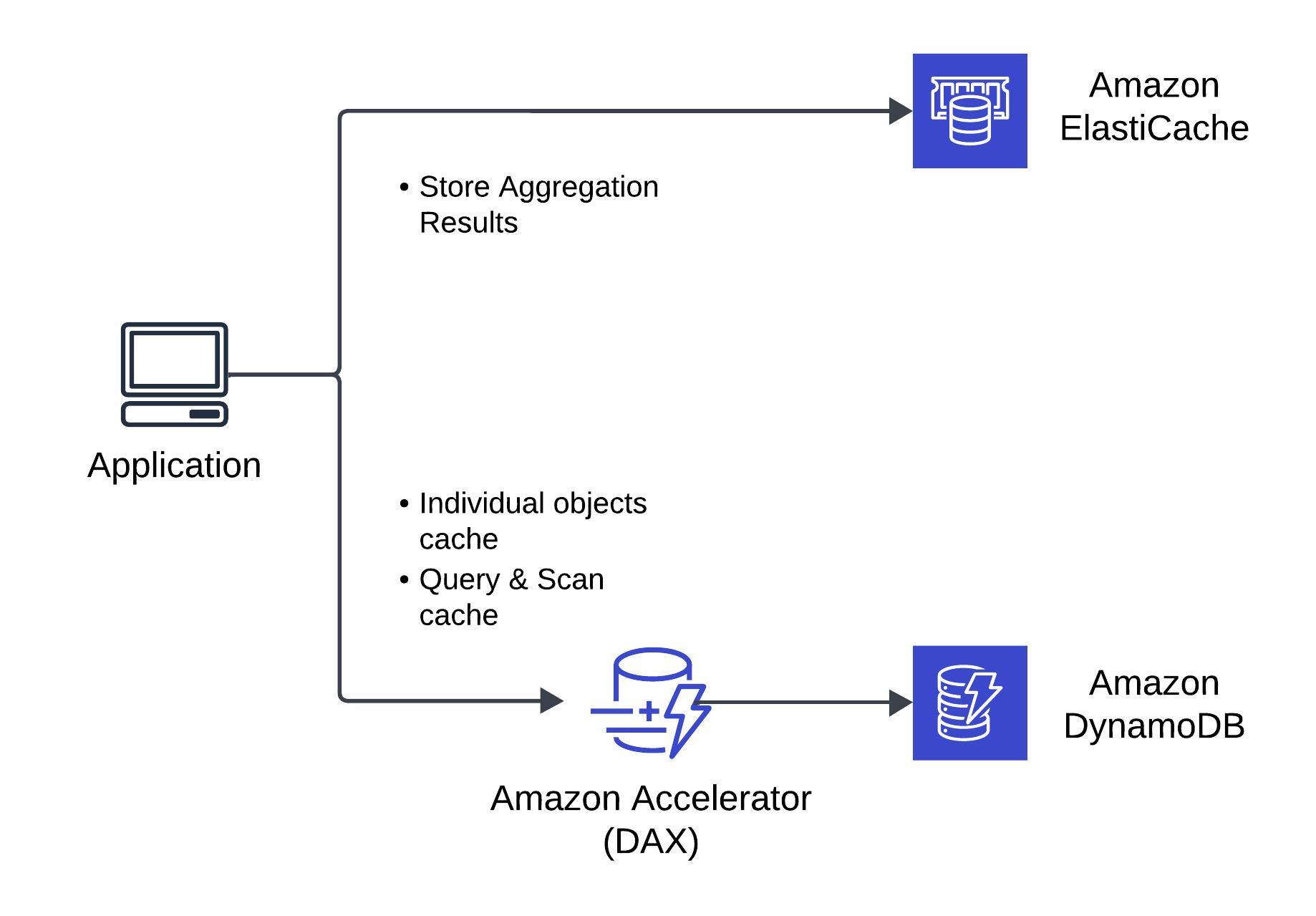
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
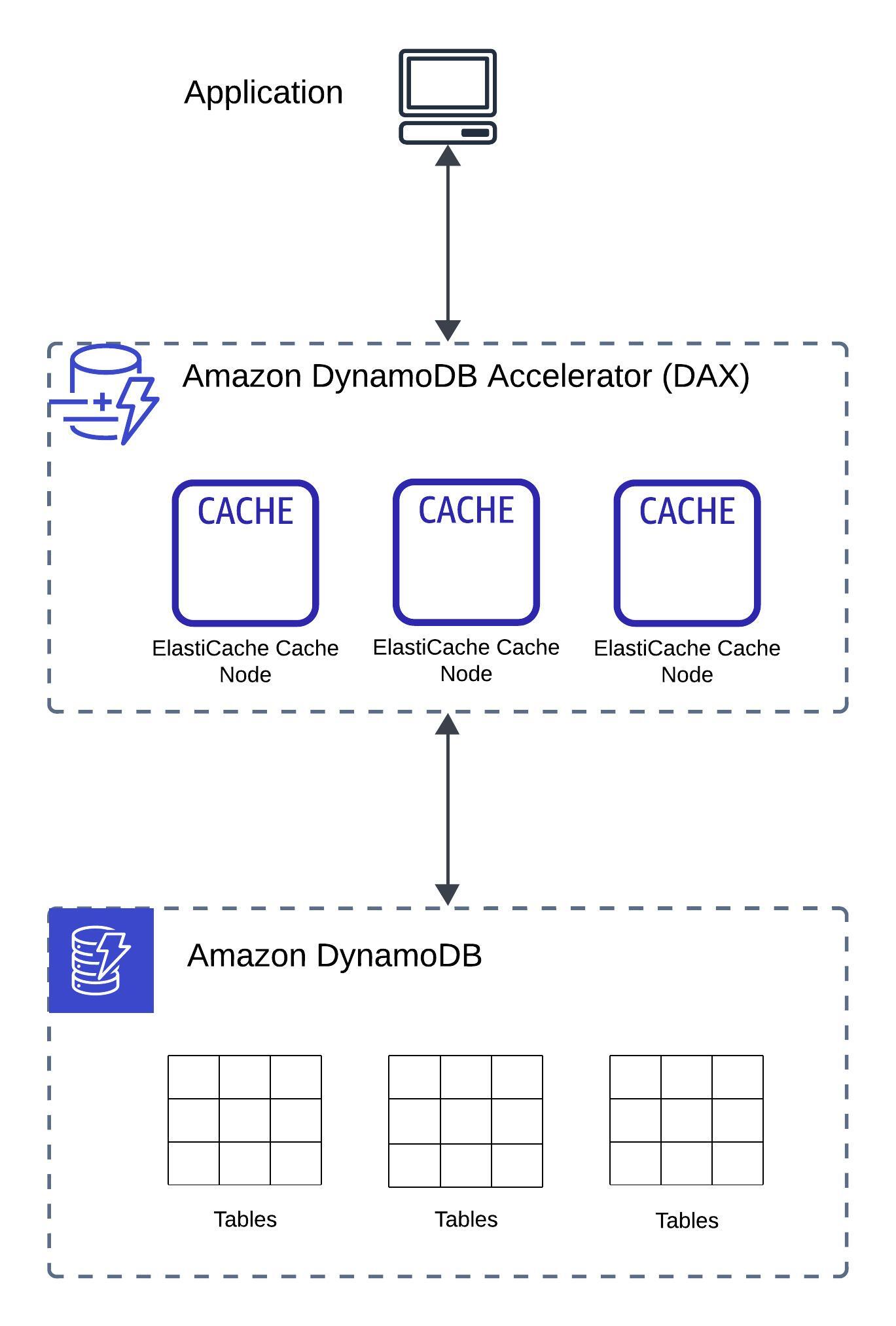
DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) vs ElastiCache
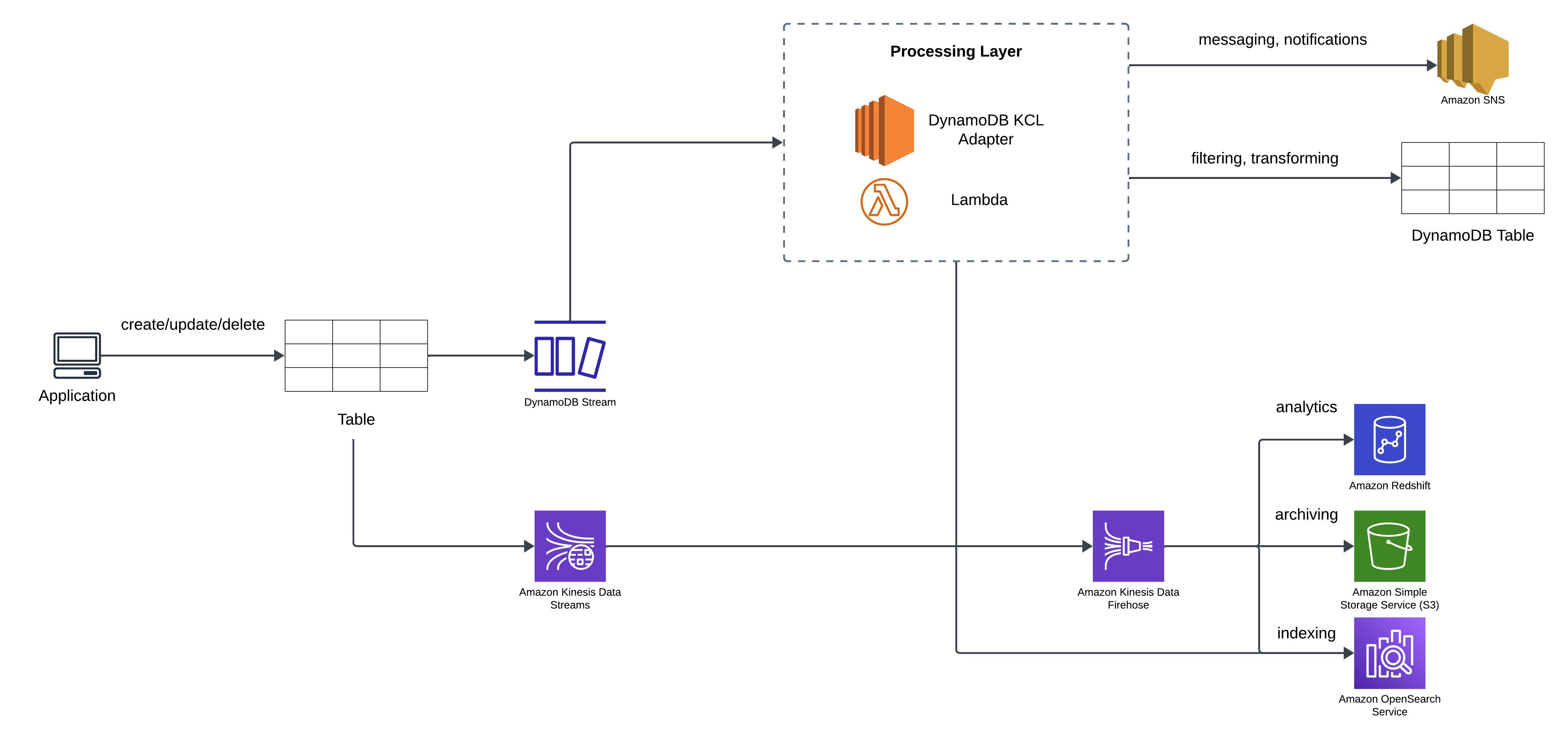
Stream Processing
| DynamoDB | Kinesis Data Streams |
|---|---|
| 24 hours retention | 1 year retention |
| Limited number of consumers | High number of consumers |
| Process using AWS Lambda Triggers or DynamoDB Stream Kinesis adaptor | Process using AWS Lambda, Kinesis Data Analytics, Kinesis Data Firehose, AWS Glue Streaming ETL... |
DynamoDB Streams
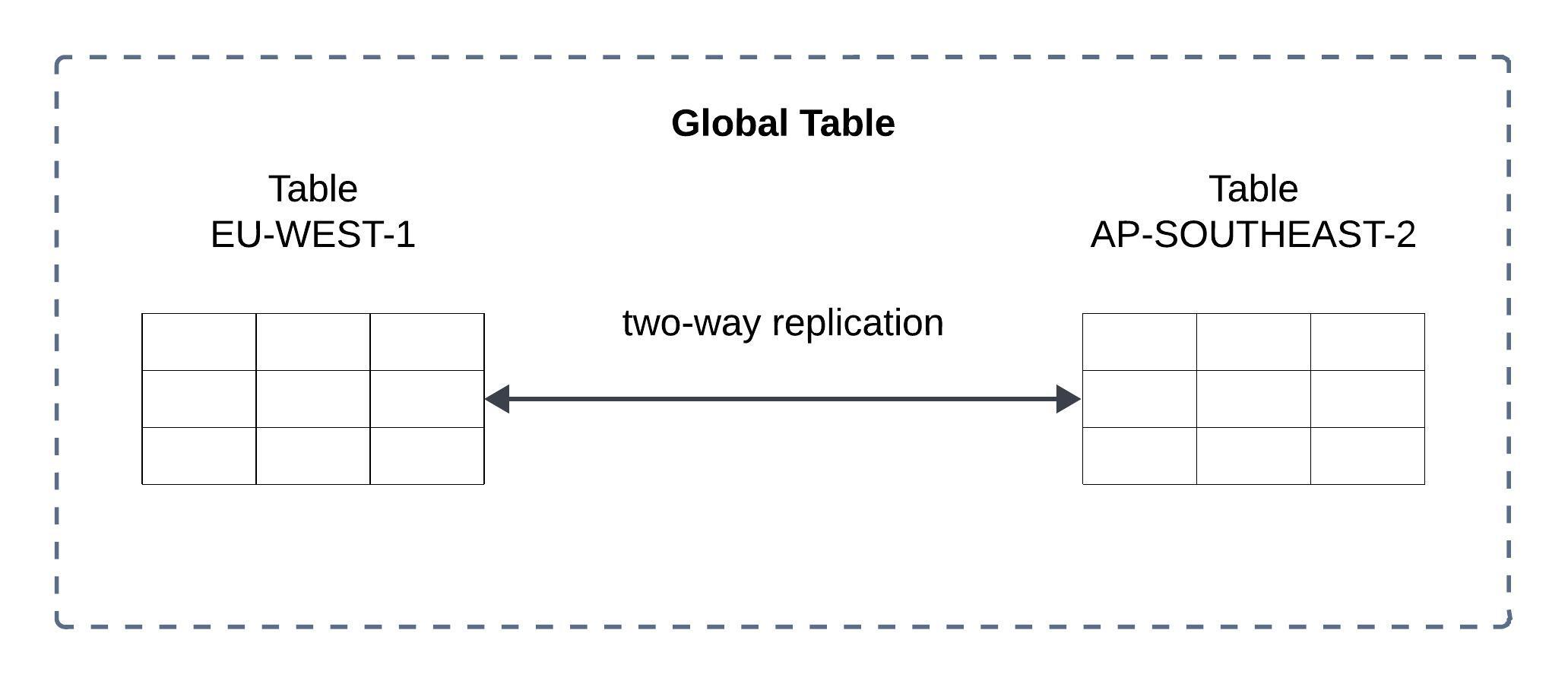
DynamoDB Global Tables
DynamoDB - Time To Live (TTL)
Automatically delete items after an expiry timestamp.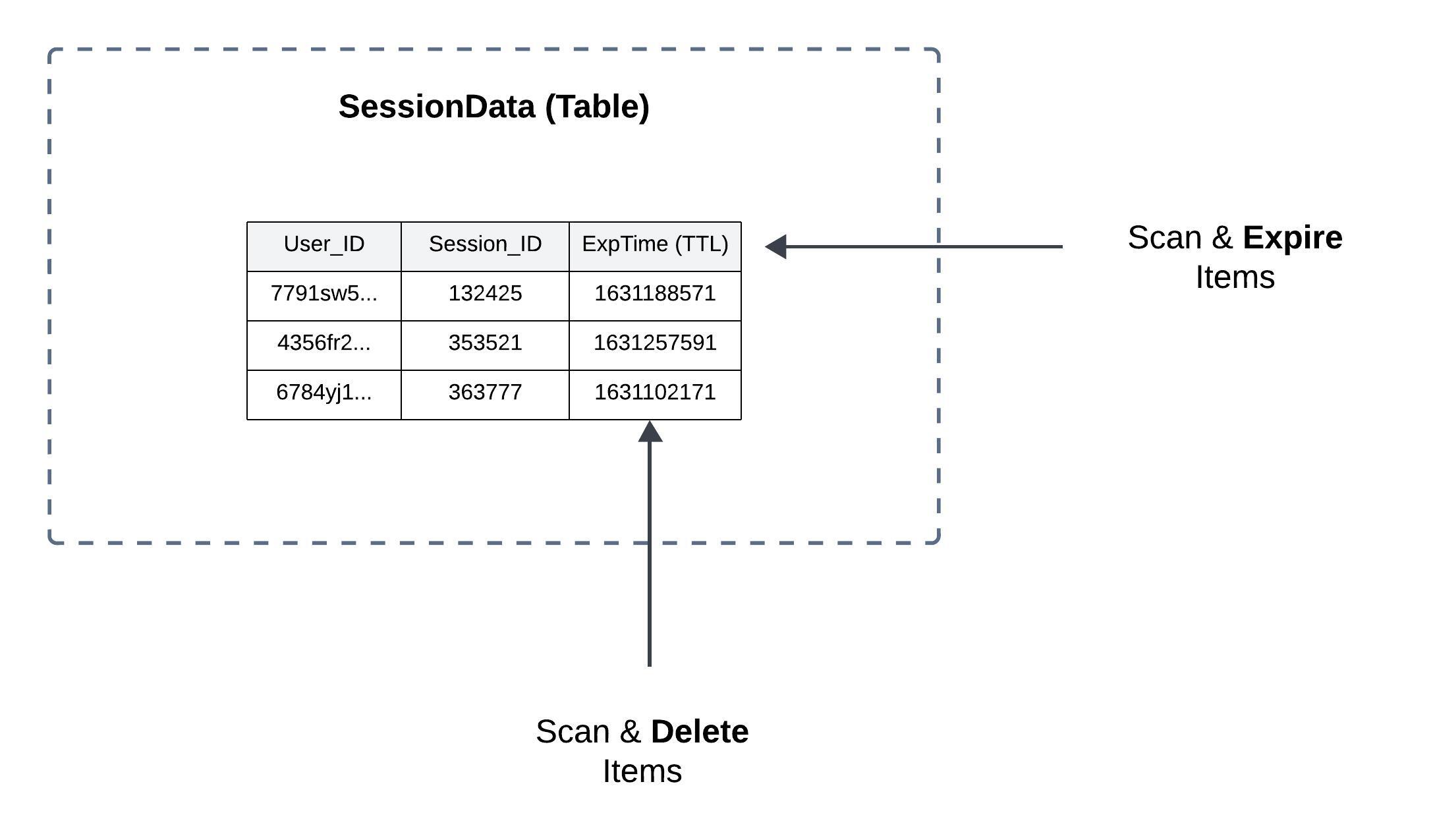
DynamoDB - Backups for disaster recovery
DynamoDB - Integration with Amazon S3
DynamoDB Summary
Amazon S3
DocumentDB
Amazon Neptune
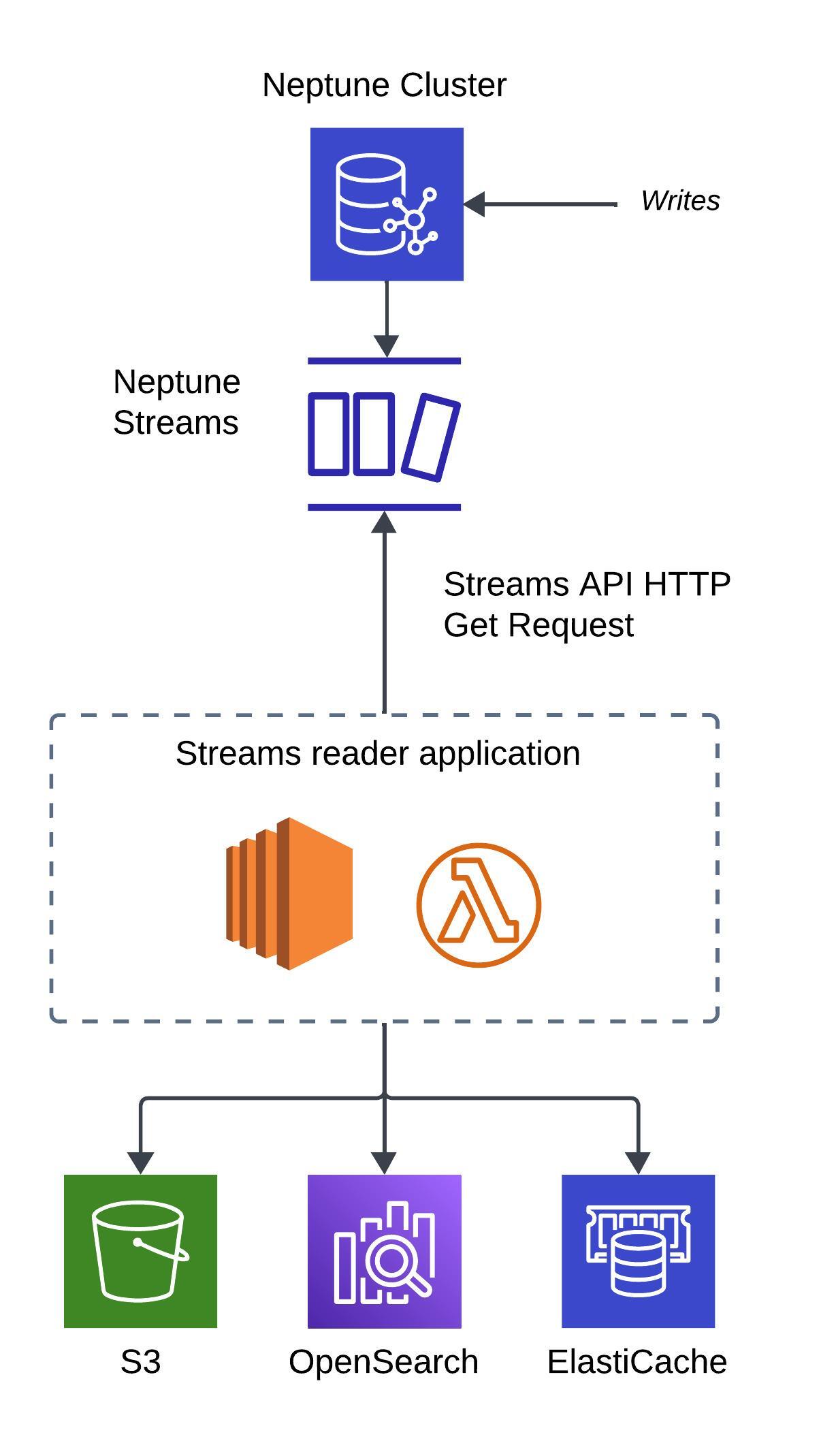
Amazon Neptune is a fully managed graph database service. It is designed to work with highly connected datasets, enabling you to efficiently store and navigate complex relationships within your data.Streams